Bioceramic Geodesic homes; The future of sustainable community-centered dwellings. ☘️🏠
The escalating climate crisis, biodiversity loss and the rising cost of housing has accelerated the need for sustainable housing solutions, and have ignited a global search for innovative building methods. There is also growing demand for homes that are energy-efficient, environmentally friendly and most importantly affordable.
The World Green Building Council estimates that around 80% of cities globally lack affordable housing for most of their population. To meet this demand, the world must construct two billion homes in the next 75 years, which equates to building 73,000 new affordable homes daily. They also laid out key principles, codeveloped by an international taskforce that can be adopted around the world, which are:
- Habitability and Comfort: homes should foster optimal health and wellbeing, by having clean air, adequate light, safe water, and comfortable acoustics, thermal conditions, and visual environments. Additionally, access to nature and walkable communities, sufficient space to prevent overcrowding, protection from evictions, destruction, and demolitions, and the encouragement of positive behaviors and choices.
- Community and Connectivity: Inclusive design, accessibility to transport and services, and fostering inclusivity and social equity are essential for creating sustainable and equitable communities.
- Resilience and Adaptation to a Changing Climate: To ensure long-term sustainability, housing must be adaptable, durable, and easy to maintain. By integrating nature-based solutions, prioritizing ecological health, and enhancing bioclimatic resilience, we can create homes that are resilient to climate change. Additionally, ensuring structural safety and considering extreme weather conditions are crucial for building disaster-resilient housing.
- Economic Accessibility: To achieve net-zero emissions, housing must prioritize whole-life carbon reduction, energy efficiency, water conservation, and waste reduction. This involves transitioning to clean energy sources, reducing energy consumption, minimizing water usage, and promoting circular economy principles.
- Resource Efficiency and Circularity: To ensure housing affordability, we must consider purchase and leasing costs, in-use costs, economic security, living costs, and development costs. This involves making housing accessible to various income levels, reducing operational costs, supporting financial stability, and promoting local economic development.
“Architecture should speak of its time and place but yearn for timelessness” Architect Frank Gehry.
From modernizing building with mud to recycling waste as a building material, many companies have been trying to solve the issue of building sustainable and affordable housings. One such company which is making affordable, earth-friendly homes with a 500-year lifespan is Geoship.
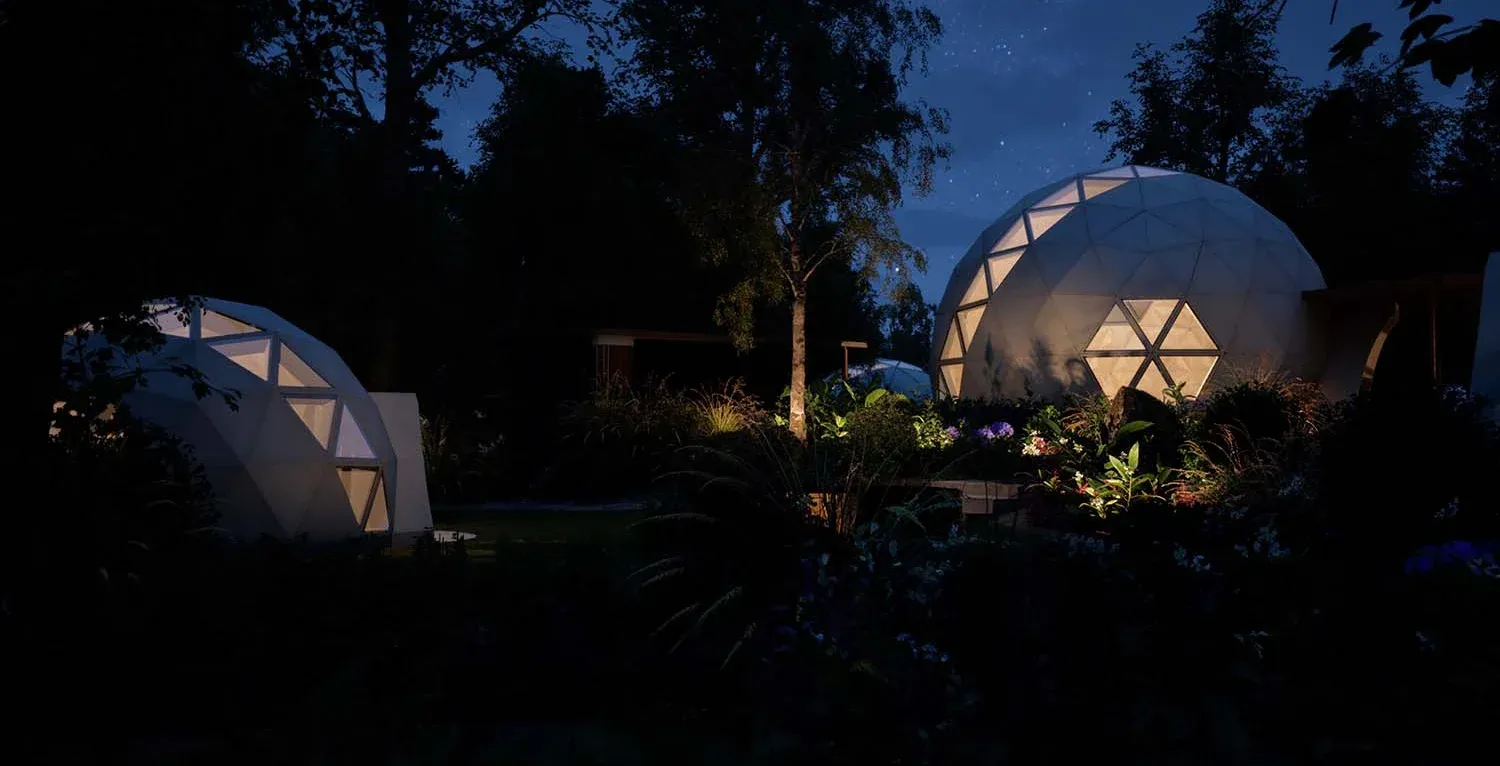
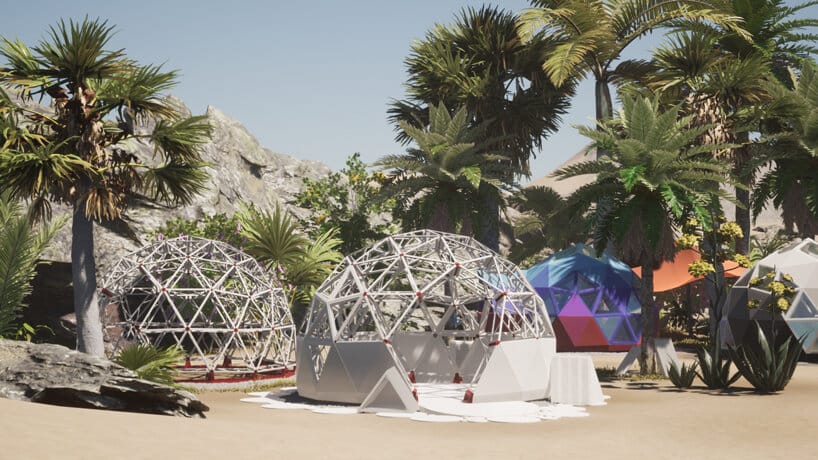
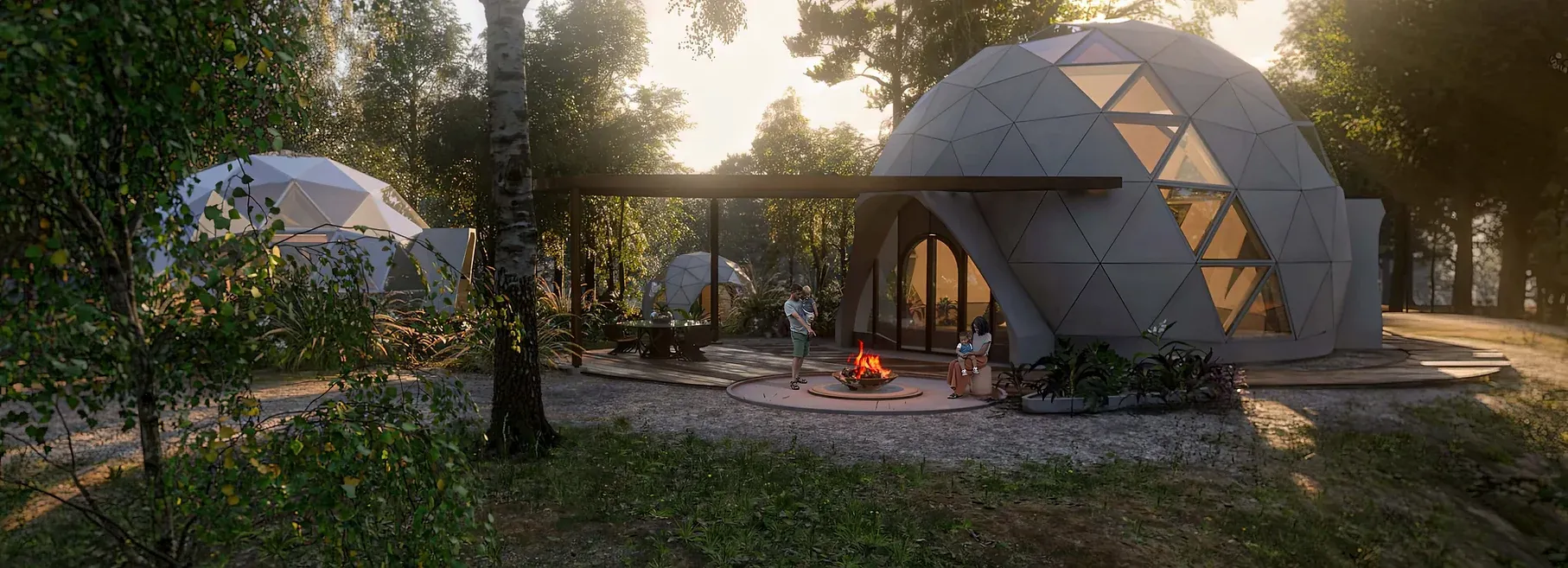



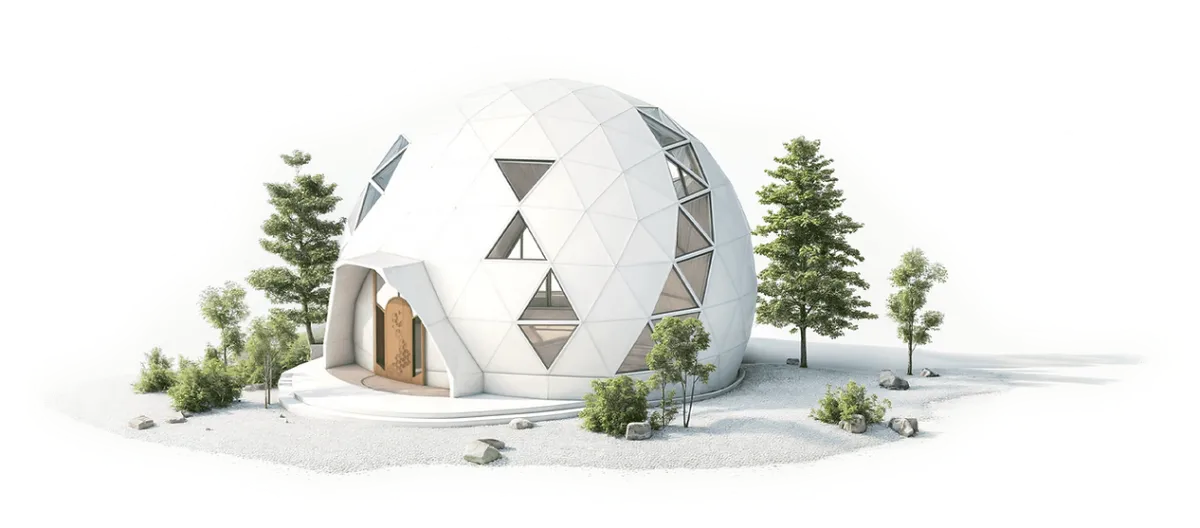
Bio-ceramic Geodesic Homes by Geoship | Source: Geoship
Geoship aims to dramatically alter the housing market by proposing the creation of domes for social housings that are affordable, energy sufficient, fire and disaster resilient. The geodesic dome that they adopted, was developed and patented by the American engineer, architect, and futurist Buckminster Fuller who anticipated that it would take more than 50 years before advancements in materials science would allow for the widespread production of these domes.
“Geodesic dome is the lightest, strongest, and most efficient means of enclosing space known to man” Buckminster Fuller.
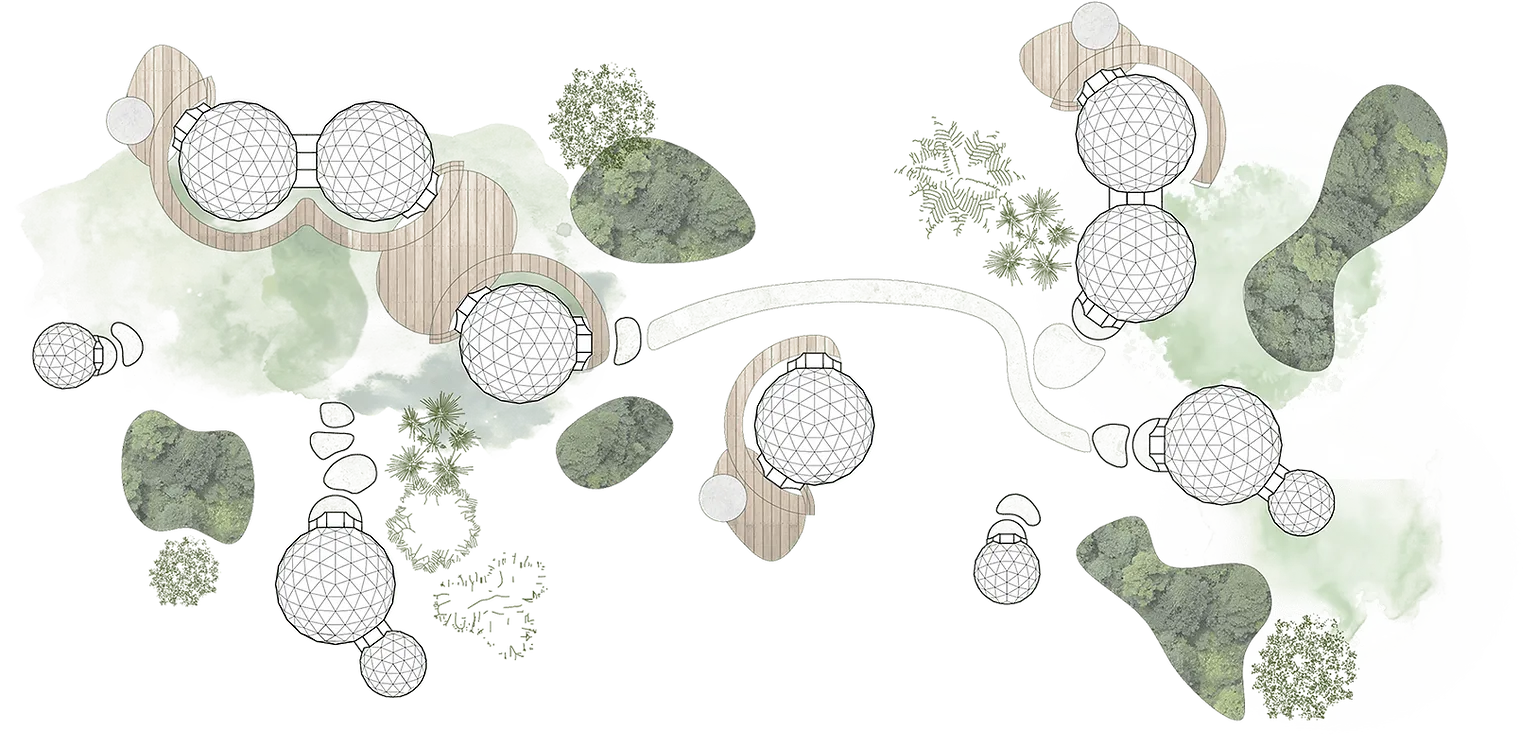
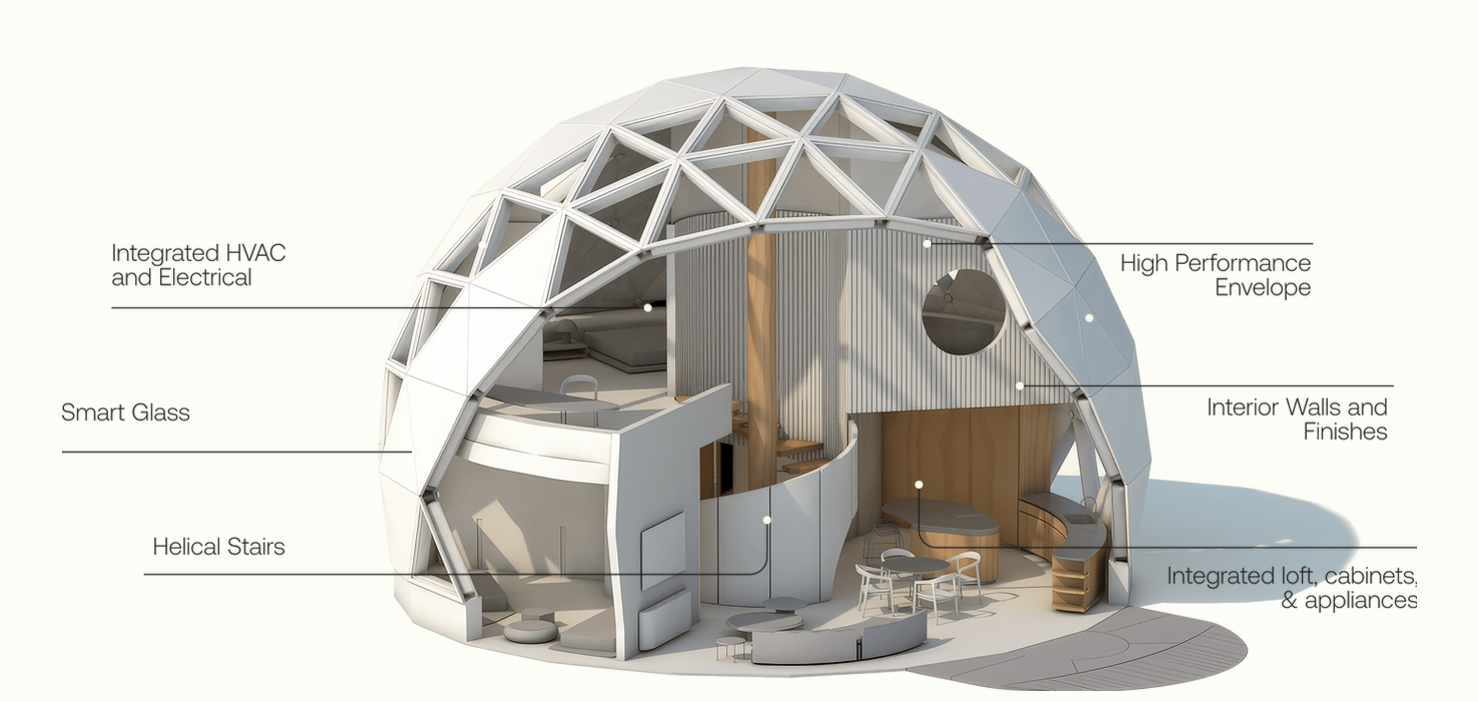
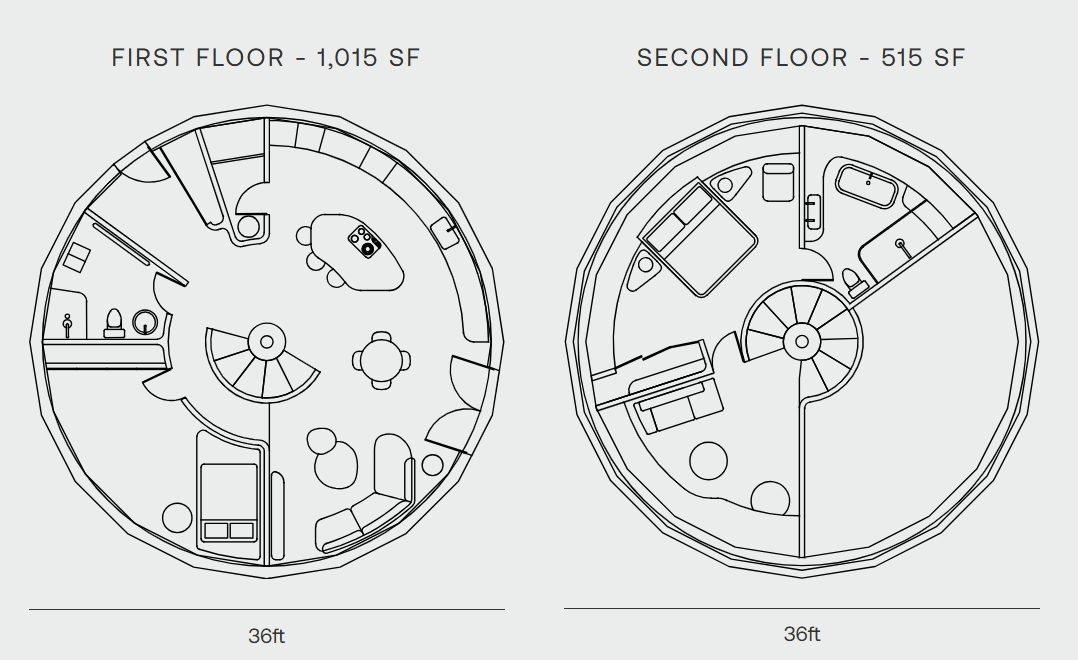
Site and Floor plans of the Geoship "Amma" | Source: Geoship
The geodesic design boasts remarkable strength, able to withstand heavy snowfall and earthquakes. The bioceramic substance that the domes are made from is a robust and non-toxic material derived from natural earth minerals and fibers. It is impervious to decay and mold, reflects heat, and offers substantial insulation. The domes are finished with a sealant of bioceramic, a waterproof inorganic polymer that resists thermal expansion, ensuring robust protection from the weather. This all-ceramic composite is not only fireproof and mold-resistant but also devoid of petrochemicals and eliminates the need for traditional building materials such as roofing, insulation, and paint. The outcome is a durable, eco-friendly living space designed for longevity. Geoship also claims that its manufacturing processes cut carbon emissions by 85% and waste by 99% compared to conventional homebuilders.
Undoubtedly, the company's dedication to sustainability and affordability, along with its aim to empower a global movement of human communities living in harmony with the Earth, will attract those who see the company as a more socially responsible investment compared to traditional modular home builders, who haven't been able to address the prevalent demands. Should Geoship realize this vision, it could play a crucial role in addressing the housing shortage and, potentially, the environmental crisis too.




Comments ()